The long branch (LB) score (Struck 2014) measures the deviation of the average pairwise patristic distance of a leaf from all other leaves in a tree, relative to the average leaf-to-leaf distance.
Arguments
- tree
A tree of class
phylo, or a list of trees of classlistormultiPhylo.
Value
LongBranch() returns a vector giving the long branch score for
each leaf in tree, or a list of such vectors if tree is a list.
Results are given as raw deviations, without multiplying by 100 as proposed
by Struck (2014)
.
Details
Struck (2014) proposes the standard deviation of LB scores as a measure of heterogeneity that can be compared between trees; and the upper quartile of LB scores as "a representative value for the taxa with the longest branches".
See also
Other tree properties:
Cherries(),
ConsensusWithout(),
MatchEdges(),
NSplits(),
NTip(),
NodeNumbers(),
PathLengths(),
SplitsInBinaryTree(),
TipLabels(),
TreeIsRooted(),
Treeness()
Examples
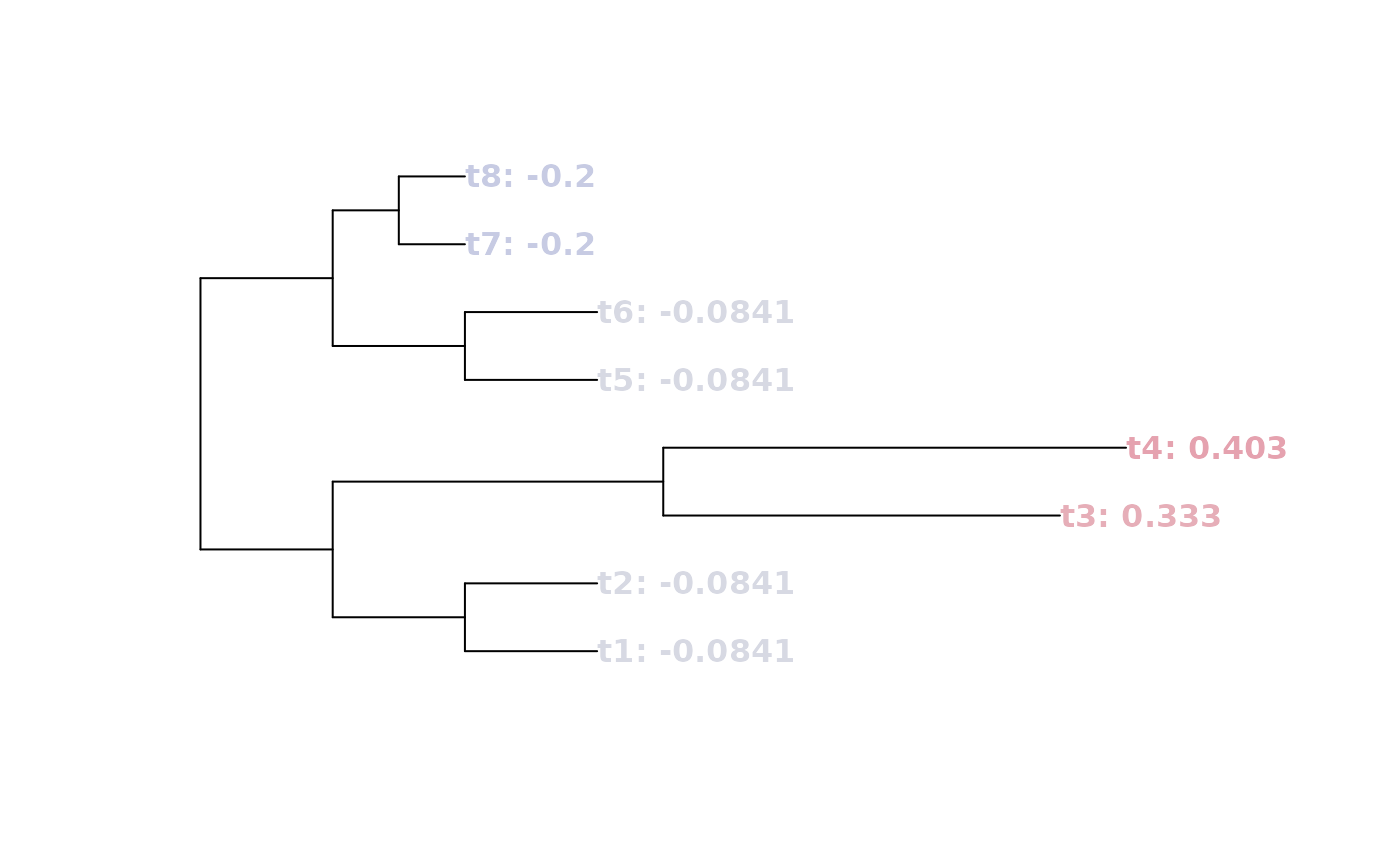
tree <- BalancedTree(8, lengths = c(rep(2, 4), 5:7, rep(2, 4), rep(1, 3)))
lb <- LongBranch(tree)
tree$tip.label <- paste(tree$tip.label, signif(lb, 3), sep = ": ")
plot(tree, tip.col = SupportColour((1 - lb) / 2), font = 2)
 # Standard deviation of LB scores allows comparison with other trees
sd(lb)
#> [1] 0.2335139
evenLengths <- BalancedTree(8, lengths = jitter(rep(1, 14)))
sd(LongBranch(evenLengths))
#> [1] 0.001698709
# Upper quartile identifies taxa with longest branches
threshold <- quantile(lb, 0.75)
tree$tip.label[lb > threshold]
#> [1] "t3: 0.333" "t4: 0.403"
# Standard deviation of LB scores allows comparison with other trees
sd(lb)
#> [1] 0.2335139
evenLengths <- BalancedTree(8, lengths = jitter(rep(1, 14)))
sd(LongBranch(evenLengths))
#> [1] 0.001698709
# Upper quartile identifies taxa with longest branches
threshold <- quantile(lb, 0.75)
tree$tip.label[lb > threshold]
#> [1] "t3: 0.333" "t4: 0.403"